1. The payoff for player 1 in current state(x,y)
2. The best response payoff for player 2 to action y, say br(y)
3. The best response payoff for player 1 to action br(y)
We use the original payoff table, Table 3, to compute 1. We then find the best response for player 2, br(y) with:
(1-Finally, we can find the best response for player 1 with:)
payoff to player 2 for 0.7, given action y +
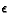
avg payoff to player 2 for any action, given state y
(1-)
payoff to player 2 for 0.7, given action br(y) +
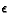
avg payoff to player 2 for any action, given state br(y)
| state/action | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | 0 | 0.0981719 | 0.126219 | 0.0841406 | 0.107313 | 0.128047 |
| 0.6 | 0 | 0.135672 | 0.126219 | 0.0841406 | 0.107313 | 0.128047 |
| 0.7 | 0 | 0.173172 | 0.201219 | 0.0841406 | 0.107313 | 0.128047 |
| 0.8 | 0 | 0.173172 | 0.276219 | 0.196641 | 0.107313 | 0.128047 |
| 0.9 | 0 | 0.173172 | 0.276219 | 0.309141 | 0.257312 | 0.128047 |
| 1.0 | 0 | 0.173172 | 0.276219 | 0.309141 | 0.407313 | 0.315547 |
| state/action | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.000390594 | 0.064235 | 0.125841 | 0.0842042 | 0.106546 | 0.12794 |
| 0.6 | 0.000392153 | 0.10187 | 0.126469 | 0.0857784 | 0.106871 | 0.127931 |
| 0.7 | 0.000392988 | 0.139585 | 0.201112 | 0.0838343 | 0.105373 | 0.127091 |
| 0.8 | 0.000391289 | 0.139366 | 0.27581 | 0.197148 | 0.108653 | 0.127637 |
| 0.9 | 0.000393105 | 0.139525 | 0.276539 | 0.307884 | 0.256177 | 0.128233 |
| 1.0 | 0.000393779 | 0.139513 | 0.276007 | 0.309145 | 0.407849 | 0.315838 |
| A. state/action | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.5 | 0.000392282 | 0.0645518 | 0.126544 | 0.0840232 | 0.107394 | 0.128128 |
| 0.6 | 0.000390676 | 0.101857 | 0.126141 | 0.0840953 | 0.107329 | 0.127883 |
| 0.7 | 0.000392615 | 0.13922 | 0.201126 | 0.0828195 | 0.107302 | 0.128218 |
| 0.8 | 0.000392658 | 0.139437 | 0.276335 | 0.196827 | 0.107078 | 0.128335 |
| 0.9 | 0.000391736 | 0.139432 | 0.276417 | 0.308681 | 0.256927 | 0.128087 |
| 1.0 | 0.000391804 | 0.139522 | 0.276431 | 0.309203 | 0.407461 | 0.315479 |
| B. state/action | 0.5 | 0.6 | 0.7 | 0.8 | 0.9 | 1.0 |
| 0.5 | 0.000391327 | 0.0984776 | 0.126531 | 0.0844144 | 0.107872 | 0.128056 |
| 0.6 | 0.000391639 | 0.136246 | 0.126278 | 0.0843203 | 0.107874 | 0.128249 |
| 0.7 | 0.000392068 | 0.173729 | 0.201349 | 0.0834542 | 0.107043 | 0.12833 |
| 0.8 | 0.000392251 | 0.173641 | 0.276331 | 0.196723 | 0.106748 | 0.127886 |
| 0.9 | 0.0003927 | 0.173609 | 0.276302 | 0.30908 | 0.257028 | 0.128126 |
| 1.0 | 0.000391546 | 0.173651 | 0.276288 | 0.308979 | 0.406666 | 0.315786 |
![\scalebox{0.78}[0.78]{\includegraphics[scale=0.53]{seq.eps}}](img31.gif)
Figure 3. Sequential, made from tables 22 and 23. The arrow indicates the Nash equilibrium of 0.7, 0.7.