 |
 |
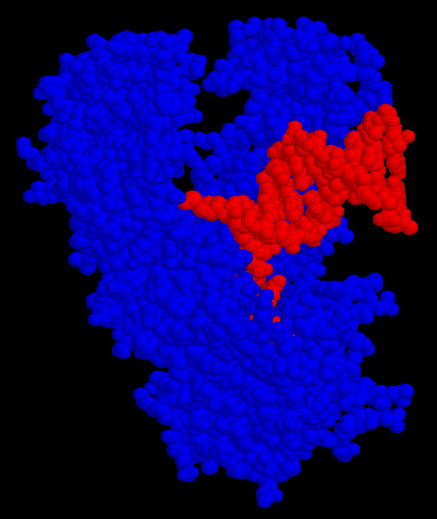
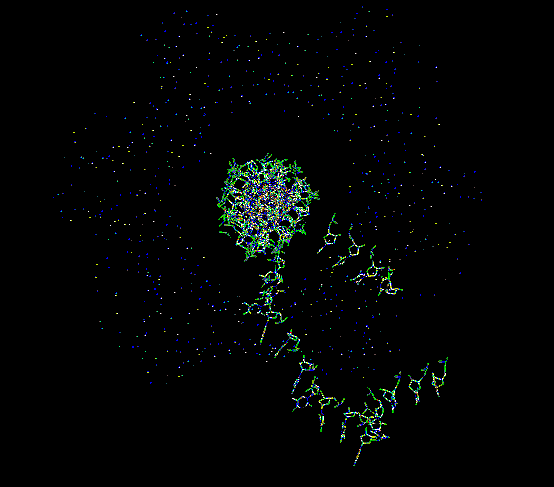
the "thumb" is in the top-right corner, and the DNA is bound to a cleft in the "palm".
DNA is made up of two helices. The are designed in such a way that given one helix, the other helix can be easily determined. Durning DNA replication, these two helicies are split apart. For each helix, the cell creates the other half. The cell taken one piece of DNA and made a copy of it. DNA polymerases catalyze this process.
DNA polymerase I (Pol I) was the first enzyme discovered to help synthesize DNA. Pol I has three main functions:
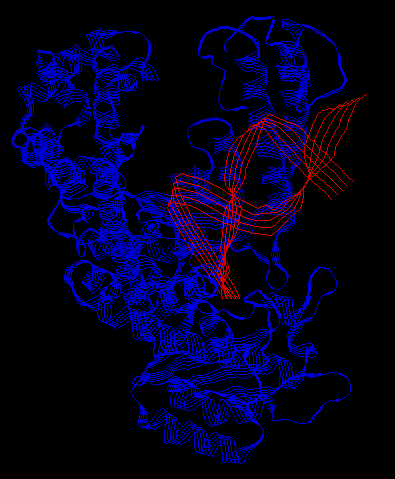
This enzyme is shaped like a hand (called the Klenow fragment). When it functions as a polymerase, it binds to the DNA just like you would grab a rod with your hand. When it functions as exonuclease 3'->5', the protein undergoes a large conformational change and forms another cleft perpendicular to the cleft that contains the polymerase site. There is yet another binding site for the third function, exonuclease 5'->3'.
The DNA also changes conformation during interaction with Pol I. As Pol I "grabs" the DNA, it bends it about 80 degrees. This is large enough that it is no longer realistic to consider it a rigid object. The DNA, as well as the protein, must be thought of as flexible.
Pol I complexed with a piece of DNA:
 |
 |
DNA polymerase III (Pol III) was discovered after Pol I. It also aids in DNA replication. This protein has a 10 subunits. One large subunit is called the beta subunit. The beta subunit consists of two c-shaped chains that interact to form a ring. Pol III binds to DNA by forming the beta ring around it. (The gamma complex -- a group of 5 subunits -- functions to open and close the beta ring around the DNA.) This ring is strongly bound to the DNA, but is is free to slide along it.
Pol III:
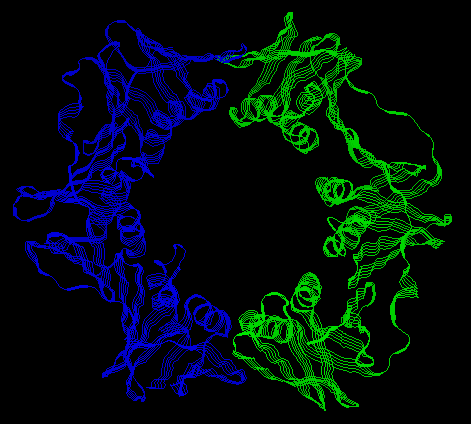 |
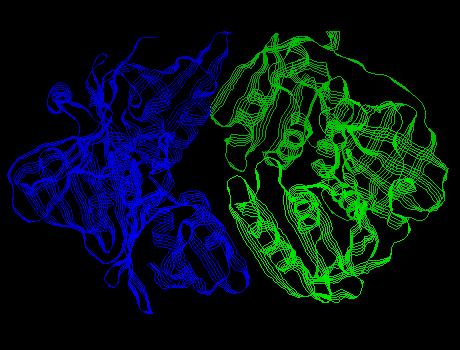 |
Pol III complexed with a piece of DNA:
 |
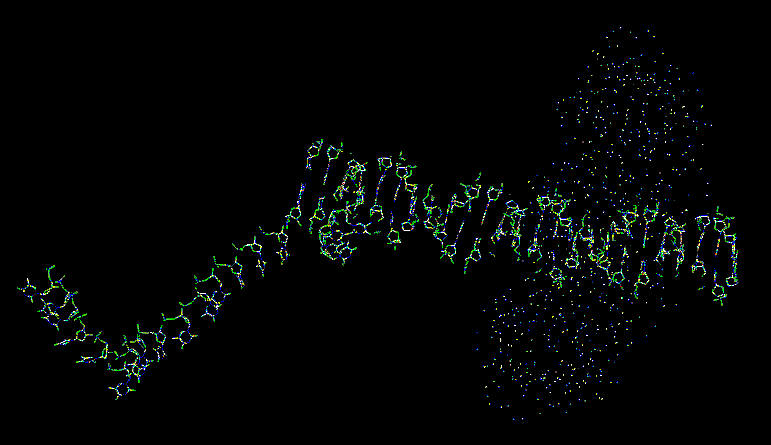 |
Last updated: 7/13/01